Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Causes And Treatment
Carpal tunnel syndrome was colloquially known as “secretary’s disease”, since it frequently affected people who perform these types of office tasks on a daily basis. However, today it could be said that it not only affects secretaries but also anyone who uses electronic devices and computers for long periods of time, such as a computer scientist, a content writer, a proofreader or an administrator, for example.
It causes numbness or pain in the wrist joint due to nerve damage in the area. Has it ever affected you? Do you want to know more about it? In that case, let’s see more below.
Carpal tunnel syndrome, a peripheral neuropathy
Carpal tunnel syndrome is actually a peripheral neuropathy. That is, its symptoms are due to damage to a peripheral nerve located in the wrist: the median nerve.
The median nerve is a sensory and motor nerve. It is responsible for the sensitivity in the palmar aspect of the thumb, index, middle and part of the ring finger. This nerve is located within a rigid structure, called the carpal tunnel.
The walls of the tunnel are made up of the bones of the wrist – the carpal bones. The upper part of the tunnel is covered by a strip of connective tissue called the transverse carpal ligament.
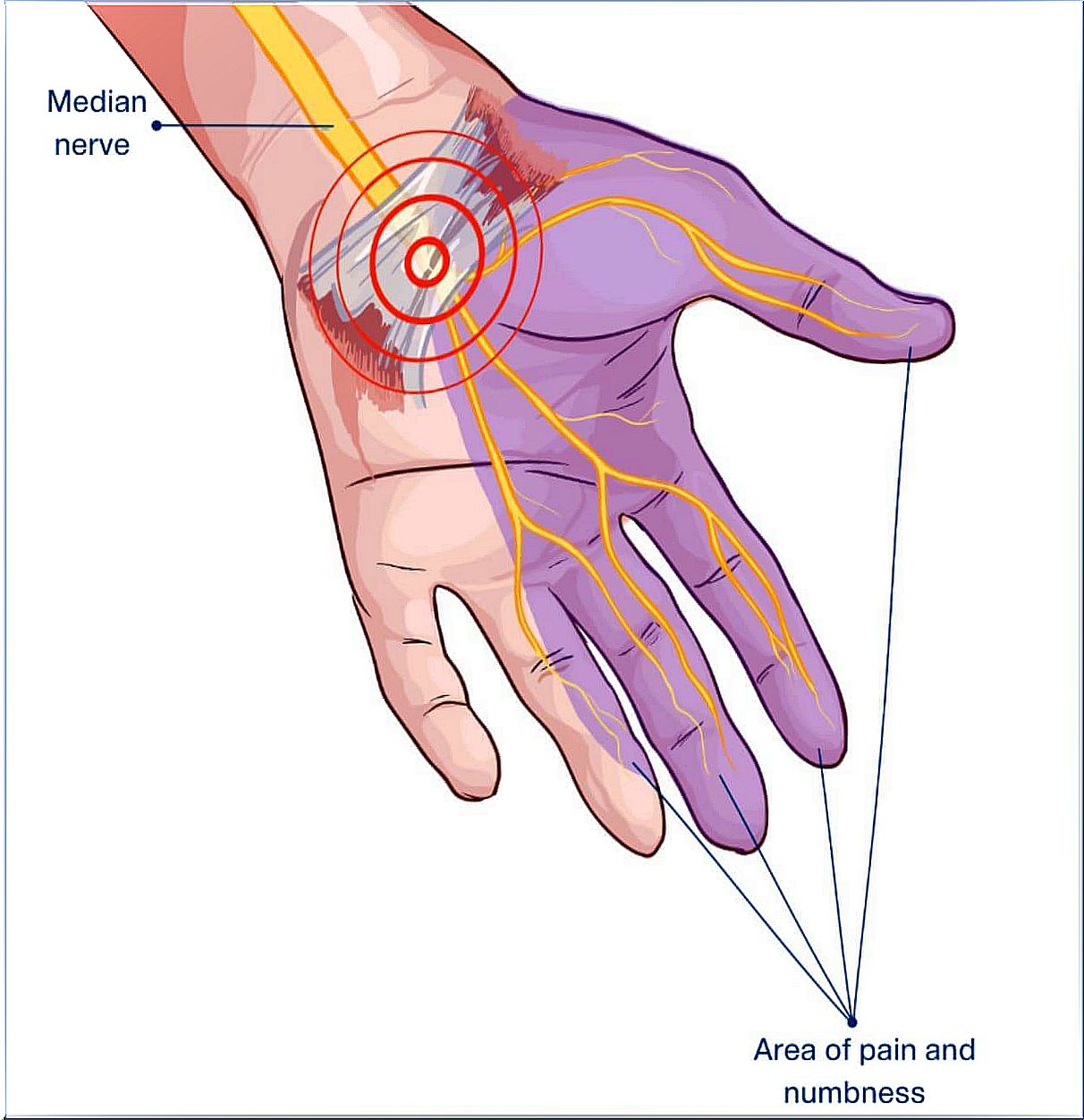
The flexor tendons, responsible for flexing the fingers, run inside this channel. In addition, in the center of the tunnel is the median nerve, which is the affected nerve in carpal tunnel syndrome.
The carpal tunnel is a narrow structure, therefore, any type of injury or swelling can compress the tendons, ligaments and nerves that are inside. When the median nerve is depressed, the pains, cramps and tingling characteristic of the syndrome appear.
Causes
The causes that cause damage or oppression in the median nerve are varied, and there may even be more than one simultaneous cause. For example, pressure on the nerve can come from an inflammation of the lining of the flexor tendons. This lining is actually the synovial membrane in charge of lubricating the tendons, allowing the joint to move.
Other reasons that can cause the condition are dislocation of the joint, the existence of fractures or arthritis. Sometimes carpal tunnel syndrome can occur from forcing or performing repetitive movements on the joint.
Other more specific causes would be the accumulation of fluids in the tunnel during pregnancy or other types of diseases such as autoimmune conditions, thyroid disorders or diabetes.
Symptoms
Some of the recurring symptoms that can occur are the following:
- Weakness in the wrist.
- Feeling of electric shock in the wrist.
- Coordination problems when moving the fingers.
- Difficulty handling, taking, and releasing objects.
- Pain in the wrist (which may extend to the elbow).
- Discomfort, pain when trying to close the hand or inability to close it.
- Tingling or numbness in the fingers or numbness in the palm.
Diagnosis
In general, to diagnose the syndrome, the doctor will do a series of physical tests that will basically consist of palpating the affected area to identify the characteristics of the pain. Your symptoms will also be evaluated and your medical history will be reviewed. Among the physical tests that will be carried out we have:
- Check for muscle weakness in the wrist area.
- Flex the wrists to identify if there is pain or weakness.
- Papping or patting the wrist to identify pain or tingling.
- Check for sensitivity in the fingers.
Sometimes other types of medical tests such as X-rays can be carried out in order to download other medical tests. As well as, electrodiagnostic tests to evaluate the speed and conduction of the nerves and thus, corroborate the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome and evaluate possible nerve injuries.
Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome
Surgery is not usually the first option, unless it is an extreme case. Certain measures are usually recommended that help reduce symptoms, such as the use of wrist braces or splints either at night or during the day. Applying hot or cold compresses to the affected area can also help.
Other recommendations include changing certain habits or bad postures that may be causing the syndrome, such as maintaining good posture when typing on the computer or being careful when developing certain sports activities that may be damaging the wrist.