Bruxism In Children: How To Act If Your Children Grind Their Teeth?
Do your children grind their teeth? The pathology is known as “bruxism” and treatment is important to avoid consequences for the teeth and the entire jaw. Find out more here.
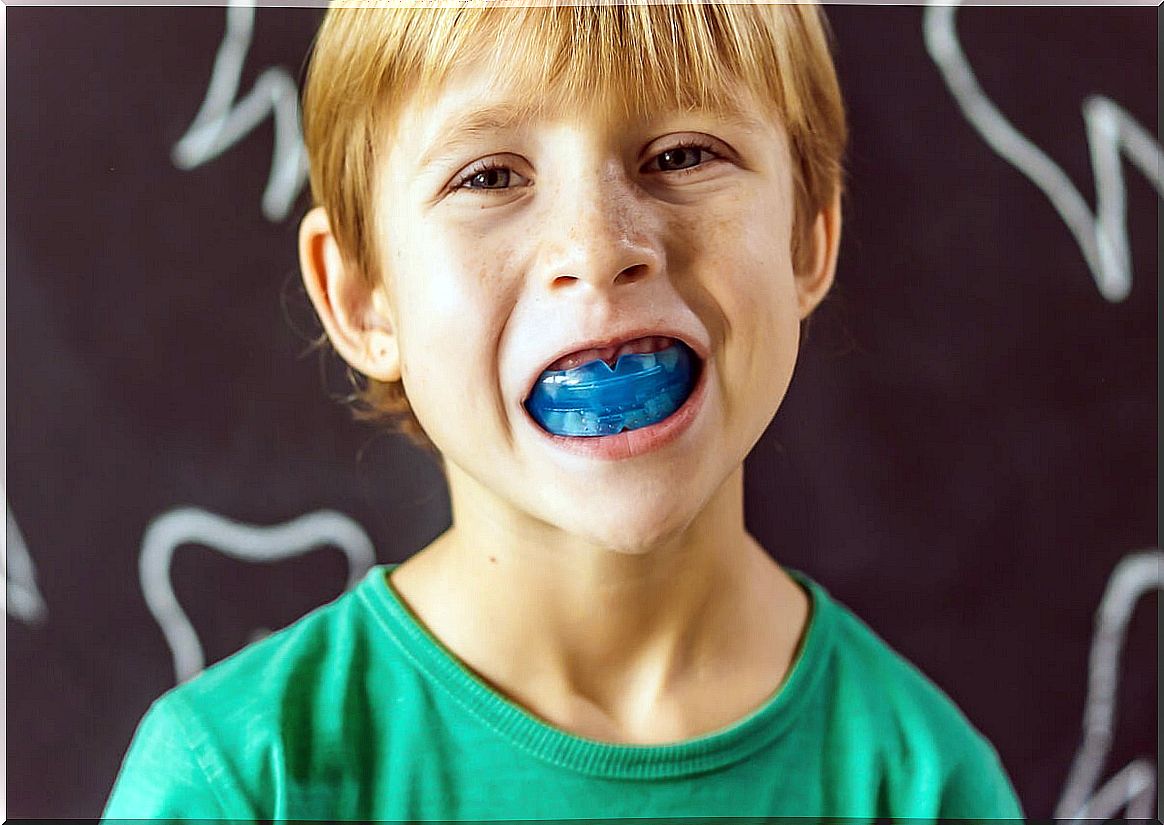

Bruxism in children can be diurnal or nocturnal. This habit, pathology or disorder has consequences. It affects the teeth and jaws, deforming the bite and causing other physical problems.
In the same way, it is a red flag, since it can denote anxiety and stress problems. In this article we tell you what it is, why it occurs and what to do if you notice that your children grind their teeth.
What is child bruxism?
The upper teeth of the denture should be as aligned as possible with the lower ones. This is what is known as normal dental occlusion. Although some overlap of the upper teeth does not constitute a faulty bite, up to a point.
On the other hand, the action of biting and keeping the mouth closed at rest should be done in a way that does not affect or deform the pieces. But this is not always the case. Some people press when closing, clenching their teeth a lot, leading to bruxism.
This term derives from the Greek word brugmos which means “bite”. Although in this case it is not about biting something, since what happens in bruxism is the opposite. It doesn’t bite, it just squeezes.
In general, it is an oral motor activity that consists of the action of closing the jaws with force, making the teeth grind against each other. When it occurs in children, it is a child bruxism.
This is a deforming habit for the teeth that is done unconsciously. It affects in various ways, causing headache and jaw pain, deforming the bite and cracking the teeth.
It can be diurnal when it takes place in situations of stress and anxiety; even during a wait or when a task is performed. But it also occurs at night, during sleep, leading to nocturnal bruxism.
Causes of bruxism in children
According to studies on the subject, there are various causes of bruxism in children. However, there is no agreement among experts on this. Several groups of factors are identified:
- Morphological: dental occlusion problems and possible joint or bone abnormalities due to bad habits or trauma.
- Pathophysiological: related to the nervous system and altered brain chemistry. Migraines can be cause and consequence.
- Respiratory pathologies: a relationship between bruxism and respiratory disorders during sleep, such as allergic rhinitis, has been determined.
- Psychological: associated with anxiety and stress. The possibility of bruxism in children is quite high when there is Down syndrome or cerebral palsy.
- Social: in some cases, bruxism in children presents with adaptive disorders when they begin to socialize or there are significant changes in their environment.
- Sleep problems: finally, nocturnal bruxism is associated with childhood sleep disorders, in which the quantity, quality and continuity of sleep are affected.
It can be said, then, that bruxism in children is multifactorial. Even the aforementioned aspects interact with each other, since anxiety and stress stimulate the nervous system, altering dopamine levels, for example, which affects rest.
How to act? Guidelines and Recommendations
Headaches and jaw pain, as well as tooth sensitivity are symptoms of bruxism to be aware of. Also, when noticing that at night there is gnashing of the teeth, the suspicion is logical.
Before detecting the situation, the first measure is to go to a specialist, both for oral health and behavior. To address bruxism in children, various therapeutic modalities are proposed:
- From a dental point of view, the use of occlusal devices (splints or protectors) is recommended while the child sleeps, in order to protect the teeth.
- Orthopedic-orthodontic treatment is usually appropriate when there are dentomaxillary abnormalities.
- Additionally, orthopedic therapies are performed to improve oral habits, working on the development of motor awareness.
- In children the use of drugs is not recommended. However, antihistamines can be administered under medical supervision when there are associated respiratory problems.
- As for the psychological approach, it is developed based on the reduction of emotional stress and anxiety.
In relation to the latter, work should be done in conjunction with the conduct professional. It is important to identify triggers for stress, be they family, personal, emotional, academic, or social.
Of course, both parents and family members who live in the immediate environment must contribute to the maintenance of a harmonious climate and a suitable environment. It is essential that the child’s sleep and emotional state are not altered.
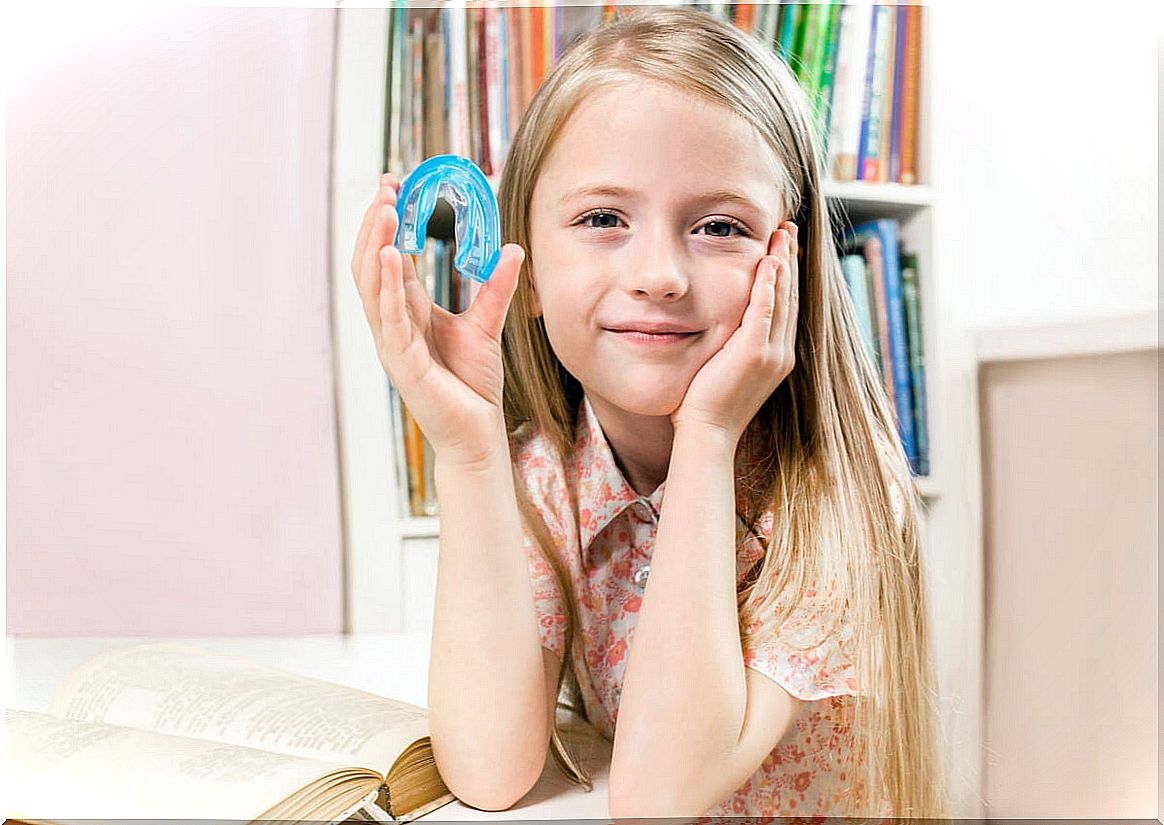

How does bruxism affect children?
In the long run, bruxism in children can have consequences of various kinds, not only for the teeth and the orofacial sector. All the muscles of the cranio-maxillofacial complex, up to the neck and shoulders, can be affected.
In the same way, since bruxism is related to behavior and sleep disorders, it should not be underestimated, considering it only as a mere dental problem, but knowing how to interpret it as an alarm signal. Therefore, considering the multiplicity of factors is key.








