Bacterial Overload Syndrome In The Intestine: Symptoms And Diet
Bacterial overload syndrome in the intestine is a disease that especially affects the small intestine. It is commonly known as SIBO , for its acronym in English, or as bacterial proliferation syndrome.
Patients diagnosed with this syndrome must follow a proper diet. It is always recommended that a health professional advise us with this, in this way the bacterial flora can be restored. First of all, it is important that we know the symptoms.
SIBO and the small intestine
Here are some characteristics that can help you better understand this disease if you suffer from it:
- The small intestine is 8 to 9 meters long and is connected to the stomach.
- It contains less than 10,000 bacteria per milliliter of fluid, while the large intestine and colon store more than a billion. It is important that this balance is never broken.
- It is an essential part of the immune system because it contains a large network of lymphoid cells that help us fight diseases and infections.
- Bacterial overload syndrome is caused by an increase in the number of bacteria in the small intestine. It can also be caused by changes in the present, since it is housed, for example, microorganisms that should be in the colon and not in the small intestine.
- This bacterial overload affects both the structure and function of the small intestine.
- For all this, digestions become heavier, nutrients are not well absorbed. We feel aches and pains as a result of an inflammation of the cells that line the small intestine.
Symptoms of bacterial overload syndrome
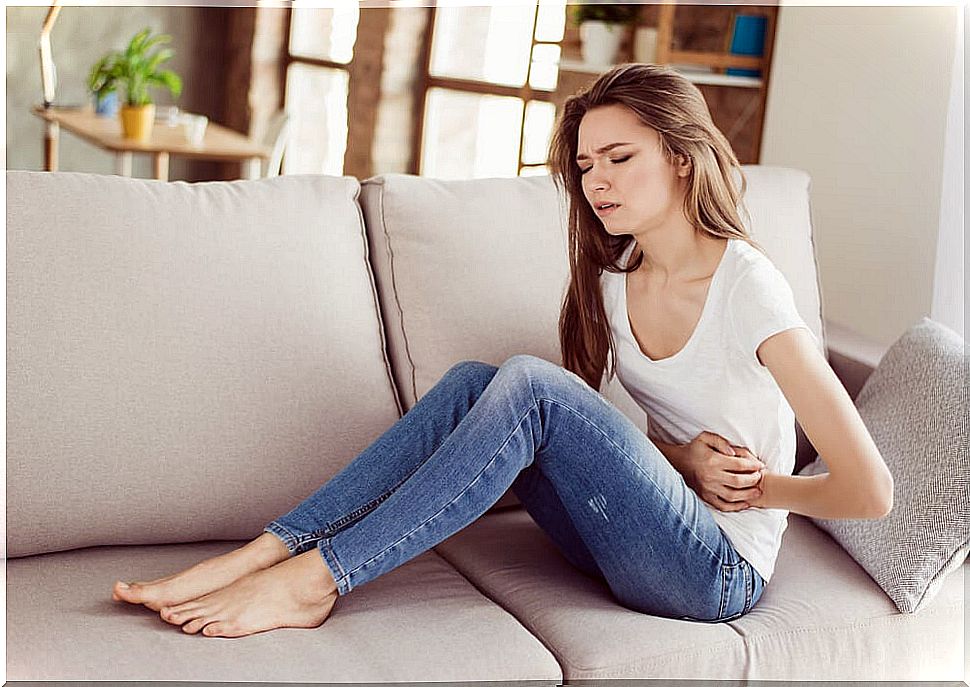

Among the most prominent symptoms we can find the following. Pay close attention to them.
Heavy digestions
The presence of bacteria that should be in the colon, but lodge in the small intestine, completely varies the digestions. By eating a few bites we will feel, for example, a very characteristic fullness and heaviness in the case of suffering from this ailment.
Digestions are slow and painful. So much so that the need to lie down to calm these discomforts is common. We must also bear in mind that we will suffer a lot of flatulence.
Diarrhea
Diarrhea is a very common part of intestinal bacterial overgrowth syndrome. Stools are almost always watery, very liquid.
Weightloss
We must bear in mind that the alteration in the cellular balance of the intestinal walls will cause a gradual destruction of the lymphoid cells.
This results in this intestinal disease attacking the immune system. We will also notice that we lose weight and suffer more infections.
Sudden intolerance to certain foods
The internal imbalance in the small intestine will cause us to not be able to digest certain foods. In turn, this drop in defenses alters the synthesis of nutrients to the point of causing intolerances. Then two things can happen:
- Bacteria present in the small intestine attack B vitamins as well as proteins.
- The internal environment in the intestine becomes intoxicated due to the accumulation of food that is not absorbed, leaving its original composition altered.
How does the body act when faced with bacterial overload in the intestine?
The body has several different ways to prevent this bacterial overload. Thus, to cope with the excessive colonization of bacteria in the small intestine, the body does the following:
- It secretes gastric acid to get rid of these pathogens.
- The muscular wall of the intestine secretes immunoglobulins to protect us.
- There is a valve that allows flow to go from the small intestine to the large intestine. It is the ileocecal valve, responsible for regulating the passage of gastric acid in just the right amount throughout the intestine.
Possible causes
The reason why some people suffer from SIBO or bacterial overload syndrome is very complex. However, the following can be mentioned as possible causes.
- Celiac disease.
- Diabetes.
- Cirrhosis.
- Pancreatitis.
- Alcoholism.
- Chemotherapy.
- Crohn’s disease.
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
- Excessive use of antibiotics.
- Taking oral contraceptives.
- An alteration of gastric acids and that acidic environment with which we protect ourselves from the accumulation of bacteria.
How to treat bacterial overload syndrome?
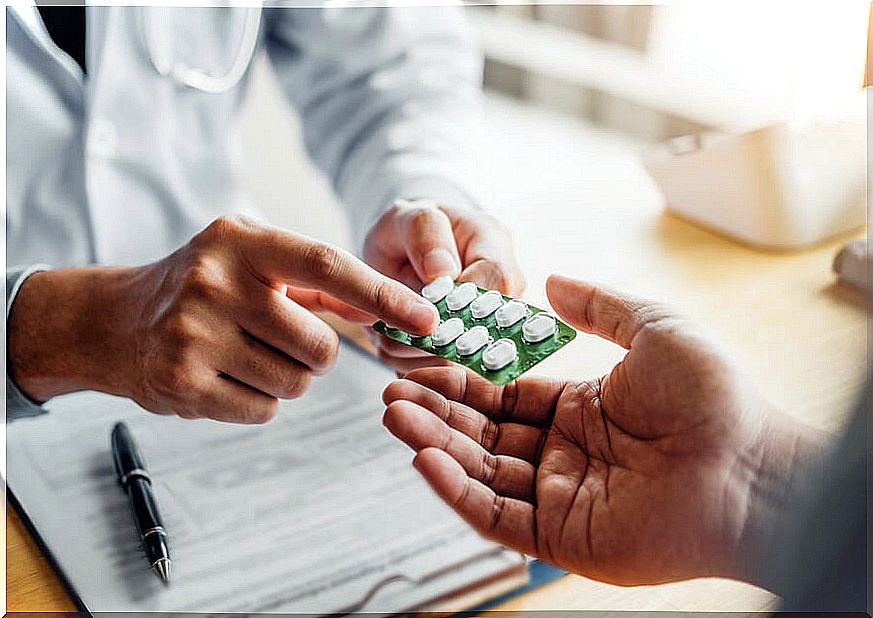

As you have seen, this ailment is related, in turn, to primary diseases. Therefore, it is essential to go to the doctor to provide us with adequate treatment.
Then, we must follow their instructions, because the treatment will not only consist of taking certain medications, but also in relying on several very simple measures, such as eating a good diet, for example.
It is worth following these basic guidelines that can help us:
- The intestines are cleaned every hour and a half to two hours. It is important to eat small amounts but several times a day, leaving at least three hours between meals.
- Avoid consuming foods with lactose and fermentable carbohydrates. They can be present not only in dairy foods, but also in fruits very rich in sugars such as: apricots, apples, pears, cherries and plums.
- Also be careful with bread, flour and cereals.
- Eat gluten-free bread.
- The most recommended fruits are: bananas, grapes, blueberries, lemons, kiwis and grapefruits.
Foods rich in vitamin B12 should also be present in the diet; pumpkins, carrots, salmon, cod liver oil, among others.
If you have questions about how to eat a healthy diet, consult your doctor.









