Symptoms Of Sporotrichosis And What Are Its Causes
Sporotrichosis is a long-term or chronic skin infection caused by a saprophytic fungus called Sporothrix schenckii . The infection develops when fungi enter the body through scratches or small cuts.
Normally, the skin and lymph nodes in the area become infected, which is why there are lumps on the skin and swollen lymph nodes. However, it rarely affects the lungs, joints, bones, or other parts of the body.
Causes of sporotrichosis

This fungus grows on rose bushes, barberry bushes, sphagnum moss, and some compost. Unlike most fungal infections, this fungus penetrates through small wounds in the skin.
In most cases, the infection occurs in farmers, rose growers, gardeners, and nursery workers. For this reason, sporotrichosis can be an occupational disease for people who work in these sectors.
Generalized or disseminated sporotrichosis can develop in people with weakened immune systems when they breathe in dust filled with spores from the fungus.
Symptoms
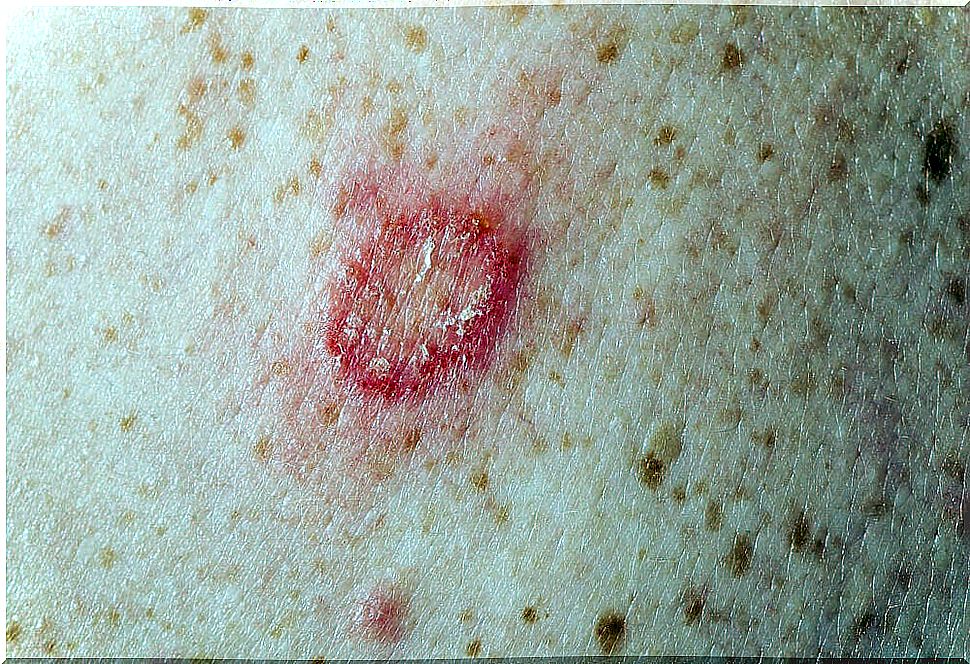
The skin infection typically begins on a finger or hand. It manifests as a small, reddish, painless bump at the site of infection. Over the next few days or weeks, the bump turns into an ulcer.
Most sores occur on the hands and forearms because these areas are commonly injured when handling plants.
The infection spreads through the lymphatic vessels of the finger, hand, and arm. Eventually, they reach the lymph nodes, forming more nodules and open ulcers along the way.
Pus from the lymph nodes may ooze through the skin. Even at this stage, it hardly causes pain. These sores do not heal unless they are treated, and they can last for years.
Infection in the lungs can cause pneumonia, with slight chest pain and coughing. This infection usually occurs in people who have a previous lung disease. In the joints it produces inflammation and makes movements painful.
Very rarely sporotrichosis spreads throughout the body. These infections are life-threatening and are more common in people with weakened immune systems.
Diagnosis
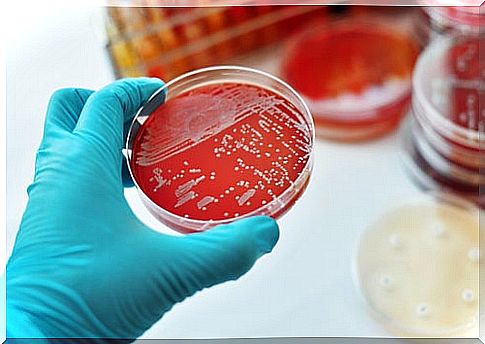
Your doctor will do an exam and ask about your symptoms. The exam will reveal the typical sores caused by the fungus. The characteristic nodules and ulcerations allow the physician to suspect sporotrichosis.
The diagnosis requires the culture of a sample of infected tissue, to confirm if the Sporothrix fungus is present .
Sporotrichosis treatment
The treatment of this skin infection is with antifungal medications. The active ingredient used is oral itraconazole, which also helps prevent the recurrence of this disease. With treatment, a full recovery is likely.
Treatment should be continued for 2 to 4 weeks even if the skin sores have disappeared. Terbinafine can also be used instead of itraconazole.
Disseminated sporotrichosis is more difficult to treat and requires several months of therapy. Infections that have spread or affect the whole body are treated with amphotericin B through a vein. In this case, the duration of treatment can last up to 12 months.
This disease can be life-threatening for people with a weakened immune system. Even if the disease is controlled, people with AIDS or other immunosuppressive diseases may need lifelong treatment.
Possible complications
People with a healthy immune system can have discomfort and secondary skin infections such as staph or strep.
In contrast, people with a weakened immune system can develop:
- Arthritis in the joints.
- Bone infection
- Medication Complications: Amphotericin B can have serious side effects.
- Respiratory and lung problems such as pneumonia.
- Brain infection
The risk of skin injury can be prevented or reduced by wearing thick gloves while gardening.