Cardiopulmonary Bypass: What It Is And What It Consists Of
Cardiopulmonary bypass is only performed under severe heart conditions, acting as its substitute.
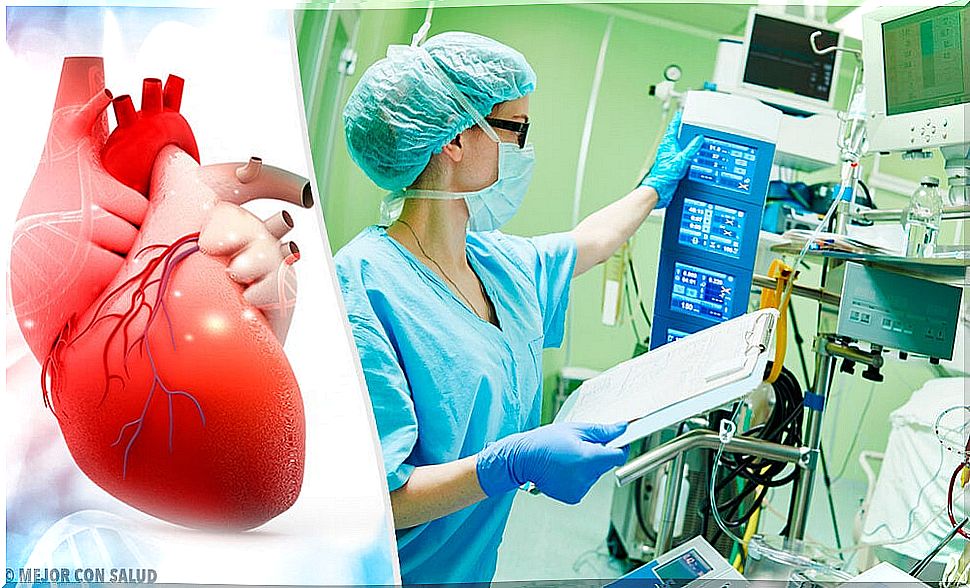
The bypass cardiopulmonary is a life – saving technique by which it is connected to the patient to a lung machine (cardiopulmonary bypass). Through this process, the patient remains alive despite the fact that his heart and lungs stop working.
The most common is that it is used during cardiovascular operations. Specifically in those that require acting directly on the heart. This is responsible for pumping blood through blood vessels throughout the body.
In this way, the arterial system allows nutrients and oxygen to reach the cells, while the venous system collects waste products and carbon dioxide.
The lungs are responsible for carrying out the gas exchange process. It is here that the blood vessels oxygenate the venous blood and remove carbon dioxide.
Cardiopulmonary bypass procedure
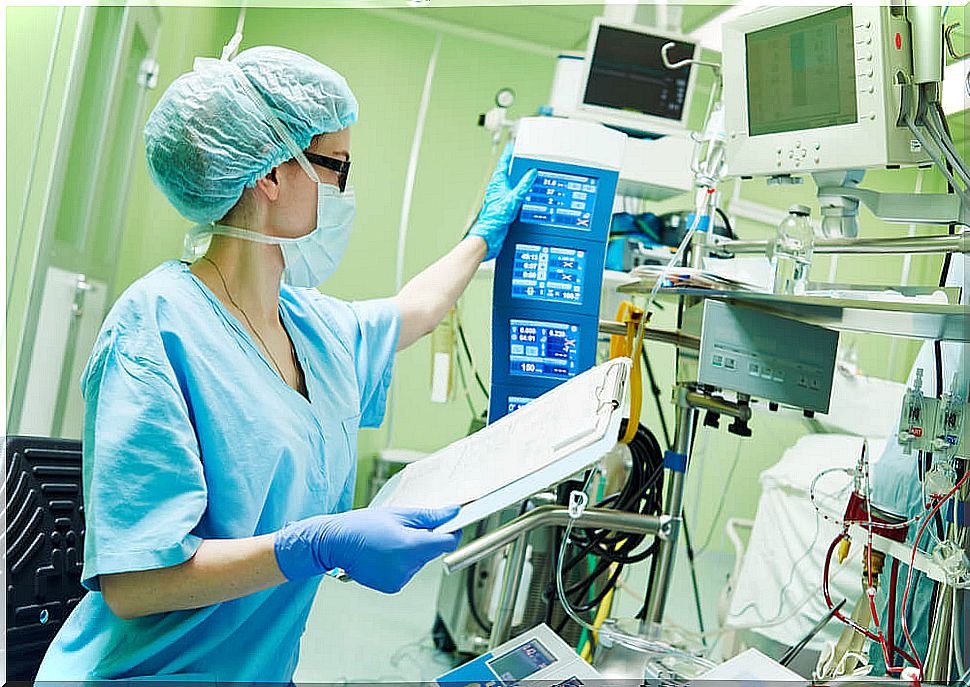
Sometimes operating on the heart while it is beating is extremely difficult for the specialist team. For this reason, the possibility of artificially stopping the heart to work more comfortably is valued .
By stopping the heart, the circulation of oxygenated blood and venous blood is blocked. Therefore, the cardiopulmonary bypass machine performs the cardiopulmonary function. The system is made up of several components: the pump, which works like the heart, and the oxygenator, which works like the lungs.
First, the patient’s chest is opened, through an incision, so that access is easier. The blood vessels leading to the heart are then connected to the oxygenator. It is made using a series of small-gauge tubes. In the device, venous blood is transformed (it is oxygenated and carbon dioxide is removed).
Finally, the pump connected to the device collects the oxygenated blood and drives it to continue its journey through the body. To do this, the aorta artery is connected to the pump through a puncture.
Side effects of cardiopulmonary bypass
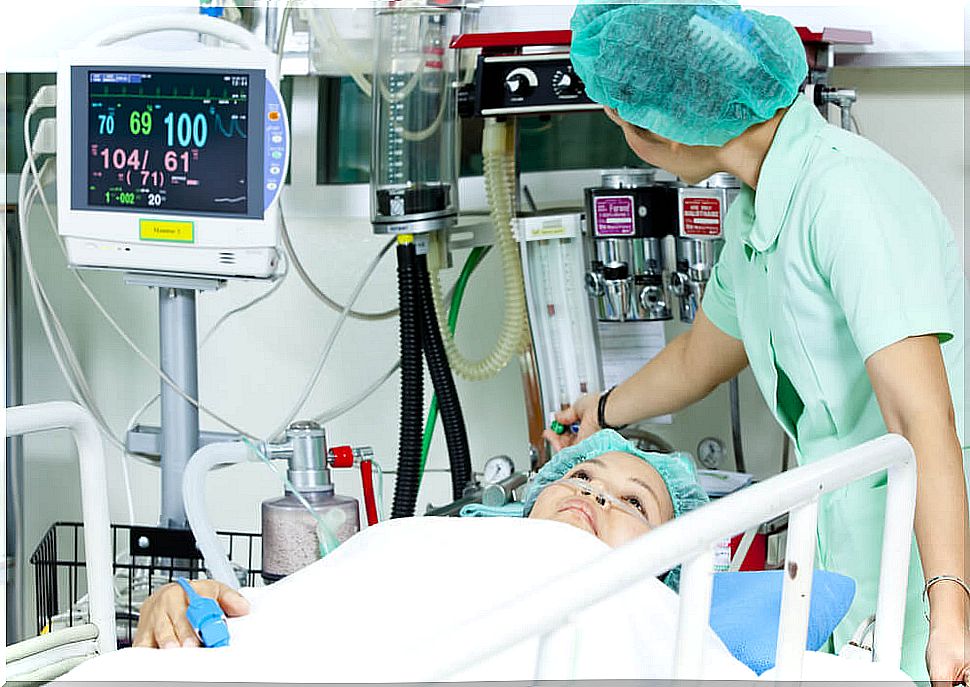
The bypass cardiopulmonary is a safe technique and in most cases is not a problem for the patient. However, any intervention carries a series of risks that must be weighed against the benefit. The most frequent complications are the following:
- Hypothermia .
- Internal bleeding
- Arrhythmias Alterations in the patient’s heart rhythm.
- Ischemia. This term refers to the loss of blood supply in a specific area. When the blood supply to the tissue is insufficient, heart attacks can occur.
- Alterations at the central nervous system level. The most common is that a confusional syndrome appears. The typical manifestations are amnesia and confusion, although in the most severe cases hallucinations may appear.
- Dysfunction of certain organs. It especially affects the kidneys since they are organs very sensitive to the loss of blood volume. This explains why the patient may suffer from acute kidney failure.
- Edema. It corresponds to the excessive accumulation of body fluids in a certain region. The tissue swells due to the ‘puddling’ produced by fluids.
- Pneumothorax. It is a lung collapse that occurs when the pleura (a thin membrane that covers and protects the lungs) fills with air. The patient has a cough, shortness of breath, and chest pain.
Prevention of cardiopulmonary bypass
Patients who undergo cardiopulmonary bypass have severe heart disease. Therefore, the most effective preventive measure is to avoid factors that increase the risk of heart disease.
Obesity is a key risk factor for developing cardiovascular disease. However, in most cases, the patient manages to lose weight by eating a balanced diet, prescribed by their doctor based on their health, etc. (since not just any diet is valid).
Regular physical activity also helps improve the patient’s physical condition and facilitates weight loss.
Finally, it is important to bear in mind that the consumption of any toxic substance irreversibly deteriorates the quality of life of the patient. For this reason, it is recommended to avoid smoking, alcoholic beverages and drugs.









