Controlling High Blood Pressure: Beyond Salt
What steps should be taken to control high blood pressure? This pathology affects billions of people around the world. Its pharmacological control ends up requiring combined therapies that involve a high health cost.
Eradicating the consumption of salt is unnecessary and insufficient. Thus, it is essential to adopt non-pharmacological measures that allow efficient control of arterial hypertension.
Current research shows that, far from restrictive guidelines, adopting a healthy lifestyle is the ideal method to control high blood pressure.
What is hypertension?
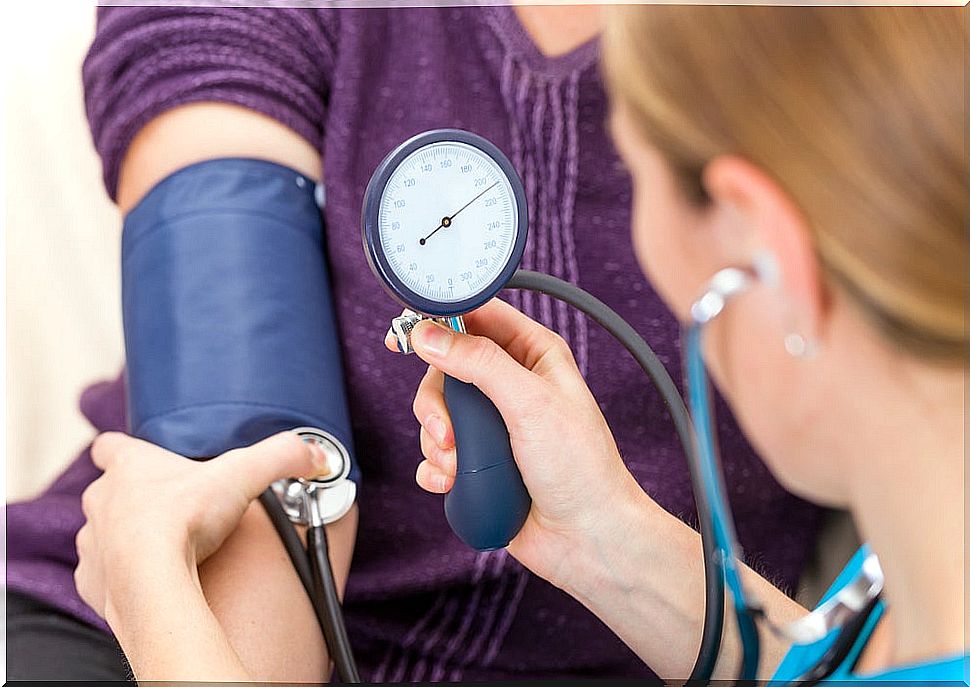
The concept of blood pressure (BP) refers to the pressure exerted by blood on the arterial walls. We speak of systolic blood pressure (TAs) to refer to the pressure existing at the moment in which the heart contracts and expels its blood to the rest of the body.
On the other hand, diastolic blood pressure (TAd) refers to the blood pressure value when the heart fills with blood. We speak of arterial hypertension (HT) when TAs> 140 mmHg and / or TAd> 90 mmHg in 3 non-consecutive measurements.
HTA affects billions of people
HTA is considered a public health problem that affects billions of people around the world. It is estimated that 30% of the population suffers from it and its prevalence exceeds 50% in subjects over 50 years of age. When not properly controlled, it ends up seriously damaging the heart, brain, eyes and kidneys, according to an article published in The Medical Clinics of North America.
In fact, HTN is considered the first cause of stroke and heart failure and the second cause of chronic kidney disease. Likewise, it is behind some of the main causes of chronic blindness. In addition, according to WHO data, HT is behind 15% of deaths worldwide.
It is clear that its control is essential. However, the high prevalence makes the cost of drug treatment unsustainable. Furthermore, the progressive need for combination pharmacological therapies leads to an increase in side effects.
What can we do to control high blood pressure?
Lifestyle is one of the factors with the greatest impact on the genesis of HTN and the good news is that it is a modifiable factor. Pharmacological treatment should be reserved for cases of HTN resistant to other measures.
Until now, non-pharmacological treatment has been based almost exclusively on reducing salt intake to avoid its attraction to fluids. But is it a necessary and sufficient measure?
Avoid salt intake is not necessary
Current scientific evidence shows that salt intake does not increase BP in all people. Some examples are:
- The study by Baker, Curhan, de Jong, Forman, Gansevoort & Scheven (2012) concluded that salt consumption only increased BP in subjects with pre-existing vascular damage.
- The research by Arós, et al. (2013) discovered that, despite its high salt content, gazpacho consumption was inversely correlated with the TA figures.
- A study carried out by Carmona, Crespo, López, Navas, Nolasco & Santamaría (2016) also found no relationship between sodium consumption and HTN
The consumption of salt only impacts on the BP of the so-called “salt-sensitive subjects” and these only represent 50% of the cases.
However, as long as the cause-effect relationship is not exactly known, and there are no tools that allow a simple detection of the aforementioned sensitive subjects, it is advisable to maintain a prudent consumption (1 teaspoon of salt per day = 5 grams of salt per day = 2.3 grams of sodium per day).
How to control high blood pressure beyond salt?
In general terms, an adequate approach to hypertension involves taking measures that: normalize the volume of fluids, reduce the viscosity of the blood, increase the caliber of the arteries or avoid arterial stiffness.
Thinking about the pressure inside a pipe can help us understand the strategy: normalize the flow, reduce impurities in the water, put larger pipes or make them of a flexible material.
Increase the contribution of potassium, calcium and magnesium
The beneficial role of potassium in controlling blood pressure is indisputable. This is because it promotes urinary sodium excretion, relaxes smooth muscle, and lowers peripheral resistance.
In other words: it normalizes the circulating blood volume and favors the adaptability of the arteries.

Calcium and magnesium have also been shown to be effective in controlling BP. Calcium allows good management of BP by inhibiting hypertensive parathyroid factor (FPH).
Magnesium does this by a mechanism that is still unknown. However, a higher incidence of HT has been detected in populations with a deficit consumption of this mineral.
Other minerals such as zinc, manganese and copper could be involved in the genesis of HTN. However, the research on this is too immature to draw any conclusions about it.
Increase your intake of fiber and protein
The consumption of 25-40 g / day of fiber has a reducing effect on BP due to:
- It decreases vascular resistance and improves the entry and exit of blood through the heart.
- It slows down the activity of an enzyme (ACE) responsible for generating a hypertensive substance (angiotensin II) and inhibiting a hypotensive one (bradykinin).
- Increases retention of hypotensive minerals such as potassium or magnesium.
- The foods that contain it are usually very rich in antioxidants and these have also been shown to be beneficial in controlling blood pressure.
Vitamins D and K are essential
The combination of low levels of vitamin D and K has been associated with an increase in blood pressure. Both appear to be actively involved in the regulation of a protein that inhibits calcification of the arteries (MGP): vitamin D increases its amount and vitamin K activates it.
This is a very novel finding (the first research in this regard was published in March 2017) and therefore further research is required. However, the research by Beulens, Brouwer, Cepelis, van Ballegooijen, van Schoor & Visser (2017), after analyzing 171 subjects, firmly concluded that both vitamins would be playing an important role in the development of HTN.
Reduce the consumption of high-glycemic carbohydrates
Excess glucose in the blood leads to an increase in the viscosity of the blood and, therefore, an increase in the TA figures. In fact, people with diabetes mellitus often end up developing HTN.
Avoid eating harmful fats
Transgenic fatty acids and most saturated fats predispose to hypertension. Its effect is due to the accumulation of cholesterol inside the arteries due to an increase in LDL protein and a reduction in HDL.
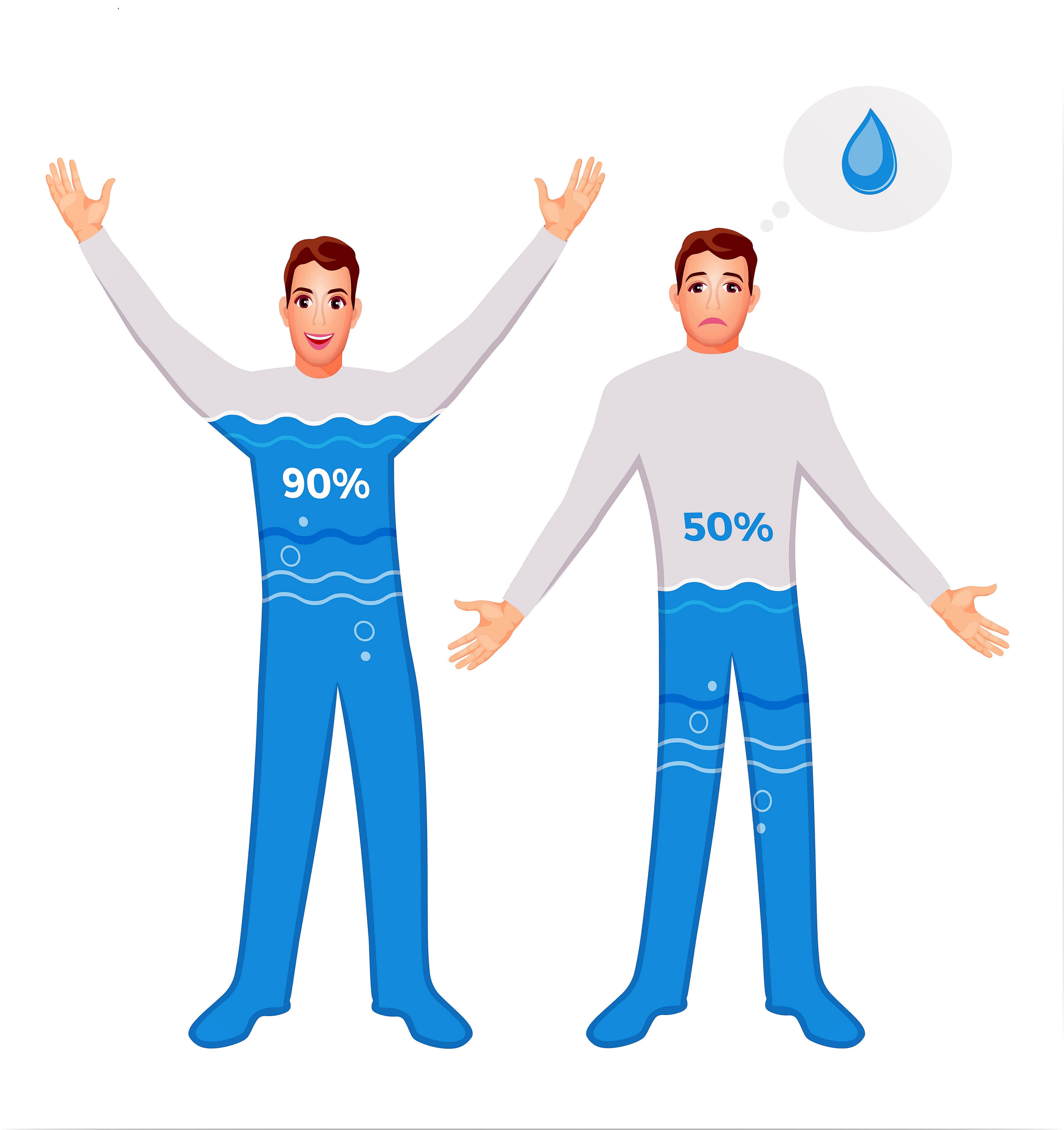
Maintaining proper hydration helps control high blood pressure
Adequate hydration favors the purification of the blood and reduces its viscosity. This means lower TA figures.

Cardiovascular physical activity is key to controlling high blood pressure
The most sedentary individuals have a 30-50% higher risk of suffering from HT. The Spanish Heart Foundation considers that cardiovascular physical activity, such as going for a walk, constitutes one of the most suitable measures for the control of BP.
Its benefits are attributed to its vasodilator effect, the elimination of sodium through sweat and its contribution to weight loss.
Excess body fat implies a risk of HTN 2 to 6 times higher, being even higher when fat accumulates in the trunk (central obesity or “apple-like”).
Ensuring an adequate night’s rest
Sleeping well is essential. Different studies link sleep problems with a higher prevalence of HT. Likewise, good sleep has been shown to help lower blood pressure levels.
Good stress management is key to controlling high blood pressure
Stress activates a whole series of hormones that stimulate the sympathetic nervous system and this is directly related to AT. Thus, learning to manage stress would entail a considerable reduction in BP figures.
Avoid tobacco and alcohol consumption
Tobacco and alcohol are toxic substances capable of increasing BP. The hypertensive effect of tobacco is due to the fact that it increases the viscosity of the blood. Alcohol does so because of its role in the genesis of various health conditions directly related to increased BP.
- Some examples are diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, and central obesity.
The intestinal microbiota is key in the control of arterial hypertension
In the same way that occurs with other chronic pathologies, those who suffer from HT share characteristics in the intestinal microbiota that have not been found in those without HT. Some hypotheses suggest that it could be due to the consumption of salt.
The study by Alm, et al. (2017) showed a lower presence of Lactobacillus in the intestinal microbiota of mice that had been given a diet rich in salt for several weeks.
The reduction of this bacterial population was associated with an increase in pro-inflammatory T (H) 17 cells and, therefore, with an increase in TA. The conclusions were identical when conducting a pilot study with 12 people. The intestinal microbiota could have the answer to why “only 50% of people with hypertension react negatively to salt consumption.”
Diet as a method of hypertension control
In terms of diet, the Mediterranean diet is ideal for applying all the nutritional recommendations mentioned. However, remember that it is necessary to maintain a healthy lifestyle that includes: sleeping well, being active, managing stress and not using toxic substances. In addition, supplementation with Lactobacillus could contribute to achieving better results.
The best way to control high blood pressure is to take a holistic approach that goes beyond just salt.