Arthrocentesis: What It Is And How Is The Procedure
Arthrocentesis is a minimally invasive procedure that rarely causes complications and instead clarifies a diagnosis of rheumatoid disease, gout, or joint infections.
Arthrocentesis is a procedure performed primarily to diagnose or supplement a diagnosis of arthritis. The objective is to collect synovial fluid, and then proceed to its study and determine what the pathology of a joint is.
Analysis of the synovial fluid obtained by arthrocentesis can establish whether the cause of arthritis is rheumatoid disease, gout, or an infection. It also helps eliminate swelling and protect the joint.
The usual thing is that before performing the arthrocentesis, a study of the patient is carried out using magnetic resonance imaging, to determine whether or not it is appropriate to perform the procedure. Although it is a minimally invasive technique, it is classified as a surgical intervention.
What is arthrocentesis?
As experts at The Nemours Foundation / KidsHealth indicate, arthrocentesis is a procedure that involves removing fluid from inside a joint cavity. This is done using a needle and syringe.
- The collected sample is subjected to study to determine if there are diseases or conditions in the joints.
- Joints are the junction points between two bones. Its main function is to allow the mobility of the skeleton.
- The joints contain synovial fluid, which is a lubricant that facilitates movement and cushions the ends of the bones, reducing friction.
The introduction of the syringe with the needle is called puncture and in arthrocentesis it is performed at the following points :
- Knee joint. It can be done in the middle area or in the lateral area, behind the patella.
- In the popliteal fossa, which is the area behind the knee.
- In the hip. It is done only exceptionally.
- It can eventually be done in any other joint, but it is very unusual.
In which cases is it indicated?
In most cases, arthrocentesis is done to help diagnose, or supplement a diagnosis of arthritis. This is a disease characterized by inflammation of the joints and causing great discomfort.

Arthrocentesis is performed for diagnostic purposes, but also for therapeutic purposes. It is indicated in these cases :
- Diagnostic arthrocentesis. When joint inflammation is suspected to be due to a bacterial infection. This condition is called septic arthritis and it is a serious condition that requires prompt attention.
- Therapeutic arthrocentesis. It helps reduce the pressure caused by the accumulation of synovial fluid. This relieves pain and discomfort. It is also usual that through arthrocentesis drugs are administered to treat the disease.
How is the arthrocentesis procedure?
Before performing the arthrocentesis there is a preparation stage in which the procedure is explained and an informed consent is signed. In general, an hour before the intervention, an anesthetic cream is placed on the puncture site, or a sedative is injected.
The procedure itself takes between 5 and 10 minutes. The patient should remove their clothing and put on a gown. They will then put you on a stretcher and clean the puncture site with a special soap. If the patient is fully sedated, his vital signs are monitored.
The doctor inserts the needle into the joint and sucks out the synovial fluid through the syringe. Sometimes X-ray or ultrasound images are used to correctly guide the movement of the needle.
Usually the syringe is sent, with the needle capped, to the laboratory. Analysis of the synovial fluid collected should be performed within 4 hours of the procedure. Sometimes it is necessary to make a new puncture to extract the remaining fluid, for therapeutic purposes.
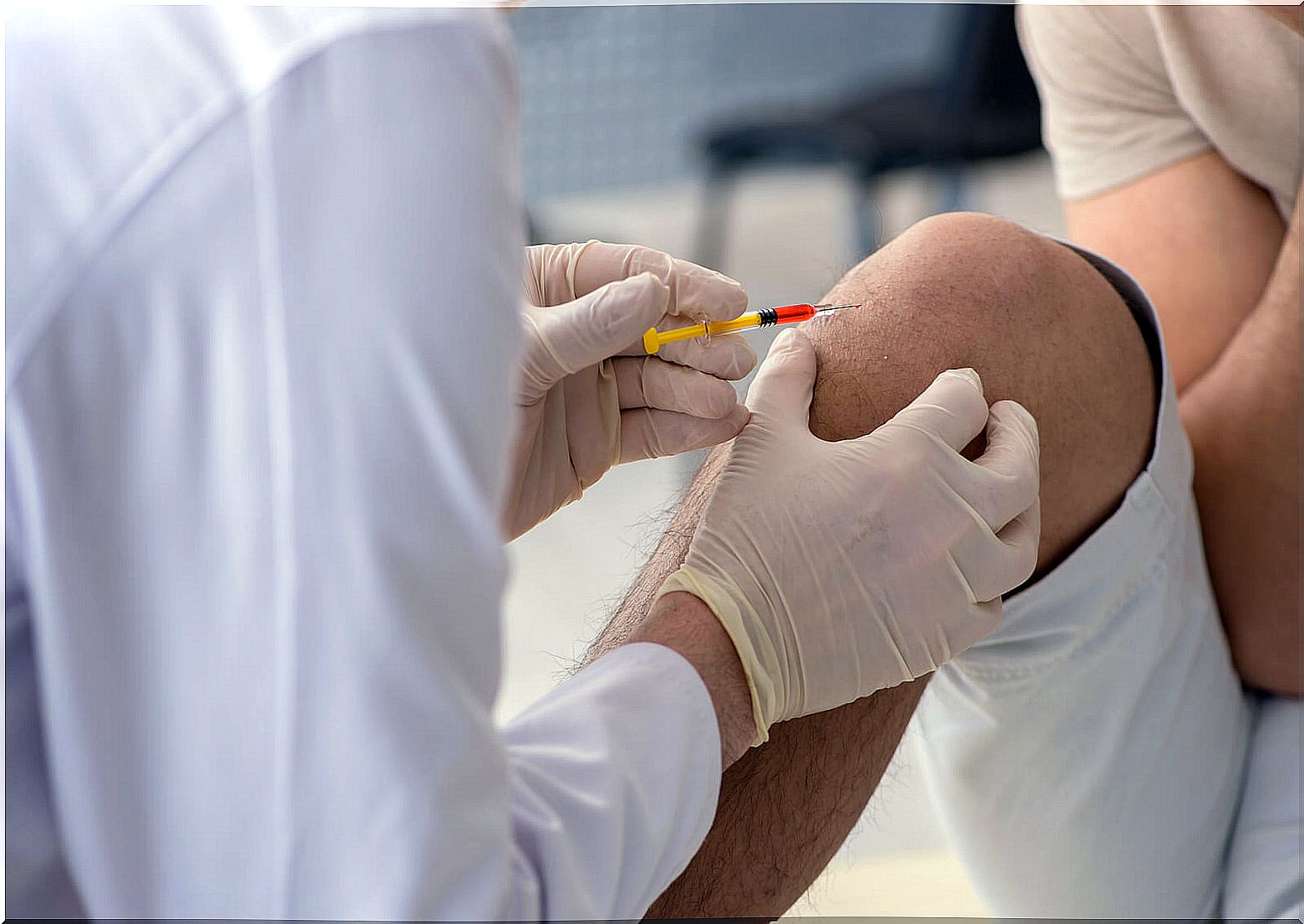
Results, risks and complications
During the laboratory analysis, a white blood cell and glucose count is made, as well as the protein level. It also checks for the presence of germs or any abnormal cells. All of this makes it possible to establish or adjust the diagnosis.
In the ER, the results are delivered in about 4 hours. Under normal conditions they take one or two days. When there are suspicions of bacterial infection , a culture is performed, which gives results in 48 hours. In these cases it is usual to start an early treatment with antibiotics.
In general, arthrocentesis is a safe and risk-free procedure. Only very rarely do problems such as bleeding or infection arise. Sedation could also cause some temporary discomfort.